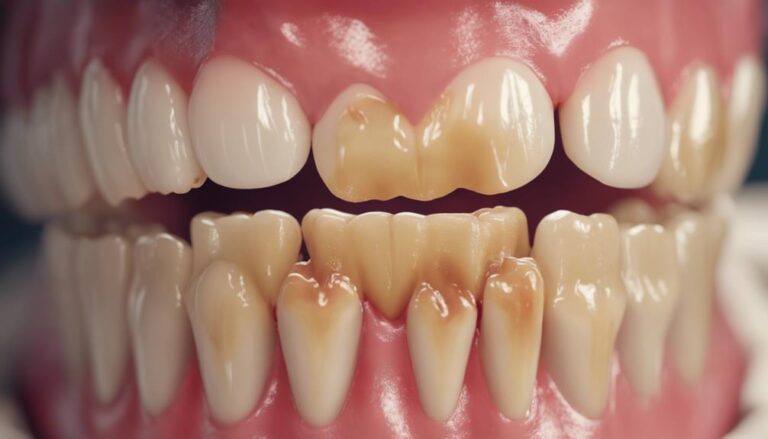
Neglecting daily oral hygiene can greatly impact gum disease development. Skipping flossing, poor diet choices, and lack of mouthwash use contribute to oral health issues. Smoking, stress, genetic factors, and hormonal changes can also increase gum disease risks. Medical conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular disease affect gum health. Balanced nutrition is essential for a healthy immune system to prevent gum disease. Maintaining consistent dental care is key for excellent gum health.
Key Takeaways
- Neglecting daily brushing increases gum disease risk.
- Proper brushing with soft-bristled brushes and fluoride toothpaste is crucial.
- Flossing daily removes plaque and prevents inflammation.
- Mouthwash reduces plaque and fights gum disease.
- Lifestyle factors like high sugar diets and smoking contribute to gum disease.
Neglecting Daily Brushing
Neglecting daily brushing greatly increases the risk of developing gum disease. To maintain excellent oral health, it’s essential to adhere to proper brushing techniques and frequency. Brushing should be done at least twice a day, using a soft-bristled brush and gentle, circular motions to clean all surfaces of the teeth effectively. Additionally, selecting the right toothpaste is important. Look for fluoride-containing toothpaste to help strengthen tooth enamel and prevent cavities.
Apart from brushing, the significance of flossing can’t be overstated. Flossing helps remove plaque and food particles from areas that a toothbrush may not reach, such as between teeth and along the gumline. This step is crucial in preventing gum disease as it reduces the risk of inflammation and infection in these hard-to-reach areas. Incorporating flossing into your daily oral hygiene routine, along with proper brushing techniques and frequency, is essential for overall gum health and disease prevention.
Skipping Regular Flossing
Regular flossing plays an important role in maintaining excellent oral hygiene and preventing gum disease by effectively removing plaque and food particles from hard-to-reach areas between teeth and along the gumline. Flossing techniques are essential for disrupting plaque buildup, which if left undisturbed, can lead to gum inflammation and disease. By incorporating regular flossing into your oral care routine, you can greatly reduce the risk of developing periodontal issues.
The benefits of flossing extend beyond just cleaning between teeth; it also helps maintain a healthy oral microbiome by removing bacteria-rich plaque that can cause harm if not eliminated. Neglecting regular flossing can result in an accumulation of plaque, leading to an imbalance in the oral microbiome and potential gum disease. Therefore, it’s important to prioritize consistent flossing to ensure excellent oral health.
Poor Diet Choices
A diet high in sugars and processed foods can contribute greatly to the development of gum disease due to its impact on oral health. Unhealthy foods, especially those high in sugars, provide an ideal environment for harmful bacteria to thrive in the mouth. When we consume sugary foods, the bacteria in our mouths feed on the sugars, producing acids that can erode tooth enamel and irritate the gums, leading to inflammation and gum disease.
Excessive sugar consumption not only fuels bacterial growth but also hinders the body’s ability to fight off infections, including those that can affect the gums. Additionally, diets lacking in essential nutrients like vitamin C, which is important for gum health, can weaken the immune system and make the gums more susceptible to disease.
To maintain good oral health and prevent gum disease, it’s important to limit the intake of unhealthy foods high in sugars and opt for a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals that support gum health.
Not Using Mouthwash
One key aspect of oral hygiene that can greatly impact gum health is the omission of mouthwash from my daily routine. Mouthwash offers several benefits that can contribute to overall oral health. It helps to reduce plaque, fight bad breath, and prevent gum disease by reaching areas that may be missed by brushing and flossing alone. Some people may choose not to use mouthwash due to myths such as it being too strong or unnecessary, but the reality is that when used correctly, mouthwash can be a valuable addition to one’s oral care routine.
If I choose not to use mouthwash, there are alternatives available such as natural mouthwashes or rinsing with a mixture of water and baking soda. However, it’s important to note that while these alternatives can provide some benefits, they may not be as effective as traditional mouthwash.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking and tobacco use greatly elevate the risk of developing gum disease and can have detrimental effects on overall oral health. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes and tobacco products impair the body’s ability to fight off infection, leading to increased susceptibility to gum disease. Nicotine restricts blood flow to the gums, reducing the delivery of essential nutrients and oxygen. Additionally, smoking weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to combat oral bacteria, which are major contributors to gum disease.
To highlight the impact of smoking and tobacco use on oral health, let’s explore the following table:
| Effects of Smoking and Tobacco Use on Oral Health | |
|---|---|
| Increased risk of gum disease | Impaired healing process in the mouth |
| Stained teeth | Reduced sense of taste and smell |
| Bad breath | Delayed recovery after dental procedures |
| Increased tartar and plaque buildup | Higher likelihood of tooth loss |
| Decreased success of dental treatments | Accelerated bone loss in the jaw |
For individuals looking to improve their oral health, consider smoking cessation programs and exploring tobacco alternatives to reduce the risk of gum disease and other oral health issues.
Ignoring Dental Check-ups
Neglecting regular dental check-ups can significantly increase the risk of undetected oral health issues and lead to more severe complications over time. Dental check-ups are essential for early detection of gum disease and other oral health problems. Regular visits to the dentist allow for professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar buildup, which can help prevent the progression of gum disease. However, factors such as dental anxiety or fear of the dentist, as well as financial constraints or lack of insurance coverage, can deter individuals from seeking timely dental care.
Dental anxiety, a common issue affecting many individuals, can lead to avoidance of dental check-ups and necessary treatments. This fear often stems from past negative experiences or a general fear of dental procedures. Additionally, financial constraints and lack of insurance coverage can pose significant barriers to accessing regular dental care. Without routine check-ups, potential oral health issues may go unnoticed and develop into more serious problems that could have been prevented with timely intervention. It’s essential to address these barriers and prioritize regular dental check-ups to maintain excellent oral health and prevent gum disease complications.
Chronic Stress
Chronic stress is a known contributing factor to the development and progression of gum disease. When under stress, the body’s immune response can be compromised, making it harder to fight off infections, including those in the gums. Additionally, individuals experiencing chronic stress may engage in unhealthy coping mechanisms like poor dietary choices or neglecting oral hygiene practices, further exacerbating the risk of gum disease.
To mitigate the impact of chronic stress on oral health, stress management techniques are essential. Strategies such as mindfulness, exercise, and seeking social support can help reduce stress levels and promote emotional health. By incorporating stress management practices into daily routines, individuals can better protect themselves against the negative consequences of chronic stress on gum health.
Prioritizing emotional well-being not only benefits overall health but also plays a significant role in preventing gum disease and maintaining excellent oral hygiene.
Genetics and Family History
Stress can impact gum health, but another significant factor worth noting is the influence of genetics and family history on the development and progression of gum disease. Genetic predisposition plays a key role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to gum disease. Research suggests that certain genetic factors can increase the likelihood of developing gum disease, even with good oral hygiene practices. Understanding these genetic predispositions can help individuals take proactive steps to prevent gum disease or manage it effectively.
Moreover, family risk factors also play an important role in the prevalence of gum disease. If close family members have a history of gum disease, there’s a higher likelihood of developing the condition due to shared genetic and environmental factors within the family. Individuals with a family history of gum disease should be particularly vigilant about their oral health and consider genetic predisposition when evaluating their risk.
Hormonal Changes
Research has highlighted the significant impact of hormonal changes on gum health. During puberty, hormonal fluctuations can lead to increased blood flow to the gums, making them more sensitive and prone to inflammation. This heightened sensitivity can result in an exaggerated response to plaque, increasing the risk of gum disease if oral hygiene isn’t maintained.
Similarly, pregnancy effects on hormones can also affect gum health. Pregnant individuals may experience pregnancy gingivitis due to hormonal changes, leading to swollen, tender gums that bleed easily.
Postmenopausal risks are another concern, as lowered estrogen levels can contribute to bone loss in the jaw and gums, potentially leading to gum disease and tooth loss. Menopause symptoms like dry mouth can also impact oral health by reducing saliva production, which normally helps neutralize acids and protect teeth from decay.
Understanding how hormonal changes influence gum health is essential for maintaining good oral hygiene throughout different stages of life.
Medical Conditions Influence
Medical conditions such as diabetes can greatly impact gum health by affecting the body’s ability to control blood sugar levels, leading to an increased risk of gum disease. Diabetes, for example, can weaken the immune system‘s response to bacterial infection, making individuals more susceptible to gum inflammation and infection. Additionally, research has shown a bidirectional relationship between gum disease and diabetes, where uncontrolled blood sugar levels can exacerbate gum disease progression, and untreated gum disease can make it harder to control blood sugar levels.
Moreover, the relationship between medical conditions and gum health extends beyond diabetes. Conditions such as cardiovascular disease and rheumatoid arthritis have also been linked to an increased risk of gum disease. These associations highlight the importance of holistic healthcare approaches that consider the interplay between systemic health and oral health.
Indeed, managing medical conditions effectively, along with maintaining good oral hygiene practices and being mindful of how dietary habits impact overall health, can significantly contribute to preventing gum disease and promoting overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Gum Disease Be Contagious Through Kissing?
Kissing can transmit bacteria present in the oral microbiome, potentially increasing transmission risks for gum disease. Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential to reduce the spread of harmful bacteria and prevent oral health issues.
Is There a Link Between Gum Disease and Heart Problems?
Yes, there is a link between gum disease and heart problems. Oral bacteria from gum disease can enter the bloodstream, causing inflammation that may contribute to cardiovascular risk. Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for overall heart health.
Can Stress Worsen Gum Disease Symptoms?
Stress management plays a vital role in gum disease symptoms. Lifestyle habits, like relaxation techniques and healthy coping mechanisms, can help alleviate stress, potentially reducing inflammation and improving overall oral health. Prioritizing stress relief for gum health is paramount.
Are There Specific Foods That Can Prevent Gum Disease?
Maintaining healthy dietary habits plays an important role in preventing gum disease. Proper nutrition is essential for oral health maintenance. Incorporating foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can help strengthen gums and boost overall oral health.
Can Hormonal Changes During Pregnancy Affect Gum Health?
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy can impact gum health. Pregnancy hormones can make gums more sensitive to plaque, increasing the risk of gingivitis. Regular dental check-ups and proper oral hygiene are essential for maintaining good oral health during pregnancy.
Conclusion
To sum up, gum disease can be caused by a variety of factors, from neglecting daily oral hygiene to genetic predispositions. It’s important to prioritize proper oral care habits and address any risk factors to prevent gum disease.
Remember, your mouth is the gateway to your overall health, so don’t let it become a breeding ground for bacteria and inflammation.
Stay vigilant in protecting your smile, as a healthy mouth truly is the window to a healthy body.