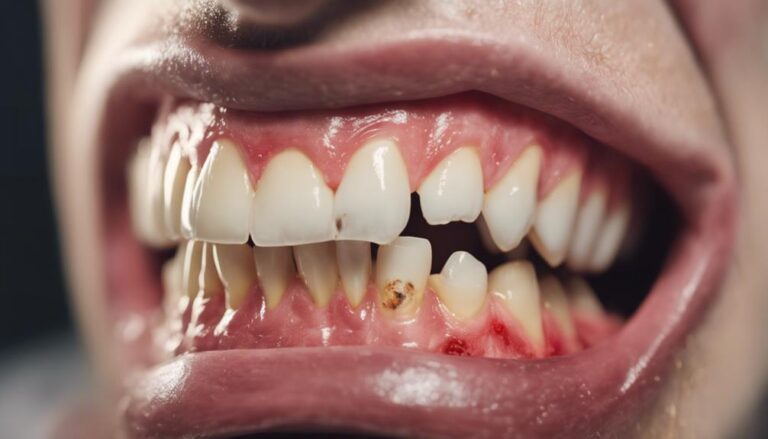
Gum disease results from bacterial infection and is linked to poor oral hygiene, tobacco use, genetics, and health conditions like diabetes. Symptoms include bleeding, receding, and swollen gums, as well as persistent bad breath. Prevention involves regular dental cleanings, good oral habits, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco. Untreated gum disease can lead to tooth loss and impact overall health. Proper management is crucial to prevent complications. Early detection and intervention are essential. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and impact of gum disease is necessary for maintaining oral and overall health.
Key Takeaways
- Bacterial infection is the primary cause of gum disease.
- Symptoms include bleeding, bad breath, receding gums, and sensitivity.
- Poor oral hygiene leads to plaque buildup, a key contributor.
- Bad breath can be a sign of underlying gum disease.
- Regular dental check-ups aid in early detection and prevention.
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition caused by bacterial infection of the gums. It’s essential to understand the treatment options and prevention methods for this condition to avoid its detrimental impact on overall health. When it comes to treatment, early stages of gum disease can often be managed through professional dental cleanings to remove plaque and tartar. In more severe cases, procedures like scaling and root planing may be necessary to clean beneath the gum line and smooth the roots to promote gum reattachment.
Prevention is key in combating gum disease. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices such as regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups can help prevent the buildup of plaque and bacteria that lead to gum disease. Additionally, a balanced diet and avoiding tobacco products can greatly reduce the risk of developing this condition. It’s important to recognize that gum disease not only impacts oral health but can also have serious implications for overall health, such as increasing the risk of heart disease and diabetes.
Common Causes of Gum Disease
Among the various factors contributing to the development of gum disease, poor oral hygiene stands out as a primary catalyst for this prevalent oral health condition. Neglecting to brush and floss regularly allows plaque to build up along the gumline, leading to inflammation and potential infection.
Additionally, skipping important dental checkups can result in undetected issues that may progress into gum disease. Effective flossing techniques play an important role in preventing gum disease by removing food particles and plaque from between teeth where a toothbrush can’t reach. Proper flossing helps to reduce the risk of gum irritation and inflammation, which are early signs of gum disease.
Regular dental checkups are essential for early detection and intervention, as professional cleanings can remove hardened plaque (tartar) that regular brushing and flossing may miss. By prioritizing good oral hygiene practices and scheduling routine dental visits, individuals can greatly reduce their risk of developing gum disease.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Maintaining insufficient oral hygiene practices can greatly increase the risk of developing gum disease. Proper brushing techniques are essential in preventing plaque buildup, which can lead to inflammation and gum disease. Brushing should be done at least twice a day for two minutes each time, using a vital soft-bristled brush and gentle circular motions to clean all tooth surfaces effectively. Alongside brushing, establishing good oral health habits like regular dental check-ups and cleanings can aid in early detection and prevention of gum disease.
Flossing is another vital aspect of oral hygiene that shouldn’t be overlooked. It helps remove food particles and plaque from between teeth and along the gum line, where a toothbrush may not reach. Incorporating flossing into your daily routine can greatly reduce the risk of gum disease. Additionally, using mouthwash can complement brushing and flossing by reducing bacteria in the mouth, freshening breath, and promoting overall oral health. By incorporating these practices into your daily routine, you can help maintain good oral hygiene and reduce the likelihood of developing gum disease.
Tobacco Use
To safeguard oral health and reduce the risk of gum disease, it’s essential to address the harmful impact of tobacco use on the mouth and overall well-being. Quitting smoking is key for maintaining excellent oral health. Tobacco use, whether through smoking cigarettes, cigars, or using smokeless tobacco, greatly increases the likelihood of developing gum disease. The chemicals in tobacco products can irritate the gums, leading to inflammation and weakening of the tissues that support the teeth. This irritation can also hinder the proper healing of gum tissues, making it harder for the gums to fight off infection. Moreover, smoking weakens the immune system, making it more challenging for the body to combat gum disease effectively.
In addition to the direct impact on gum health, tobacco use is a leading cause of bad breath. The chemicals in tobacco products can linger in the mouth, causing persistent bad breath that can be difficult to eliminate. Taking steps to quit smoking not only benefits your oral health but also improves your overall well-being. Make the decision to quit smoking today to protect your oral health and reduce the risk of gum disease.
Genetics and Gum Disease
The influence of genetics on gum disease susceptibility becomes increasingly apparent in individuals with a family history of oral health issues. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in determining an individual’s likelihood of developing gum disease. If there’s a family history of gum disease, one may have a higher risk due to inherited genes that affect the immune response to bacteria in the mouth. While genetics can predispose someone to gum disease, it doesn’t guarantee its development. Understanding one’s genetic predisposition can help in taking preventive measures such as maintaining good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and lifestyle adjustments like quitting smoking, which can exacerbate gum disease.
When considering treatment options for gum disease, individuals with a genetic predisposition should be particularly vigilant about their oral health. This may involve more frequent professional cleanings, specialized treatments, and diligent home care routines. By being proactive and aware of one’s genetic risk factors, one can effectively manage gum disease and prevent its progression.
Hormonal Changes
Experiencing hormonal changes can significantly impact the health of your gums and contribute to an increased risk of developing gum disease. Hormones play an essential role in maintaining the balance of the oral environment. During puberty, pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause, fluctuations in hormone levels can lead to changes in blood flow to the gums, making them more susceptible to inflammation and infection.
Pregnancy hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, can increase blood flow to the gums, causing them to become more sensitive and prone to gingivitis. This condition, known as pregnancy gingivitis, can result in swollen, tender gums that bleed easily. Additionally, hormonal changes can affect the body’s response to bacteria, making pregnant individuals more vulnerable to gum disease.
It’s vital for individuals experiencing hormonal changes to maintain good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups to prevent gum disease and ensure excellent oral health.
Medications and Gum Health
Fluctuations in hormone levels can impact gum health, and the effects of medications on oral health are important to take into account as well. When considering medications and gum health, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects that certain drugs can have on your gums. Some medications may cause gum inflammation, overgrowth, or even lead to gum disease. It’s necessary to inform your dentist about all the medications you’re taking so they can monitor your oral health effectively.
Prevention is key when it comes to medication-related gum issues. Maintaining a good oral hygiene routine, including brushing, flossing, and regular dental check-ups, can help prevent or minimize any medication-induced gum problems. Additionally, being mindful of any prescription drug interactions that could affect your gum health is crucial.
If you notice any changes in your gums while taking medications, don’t hesitate to consult your dentist for appropriate treatment. Remember, proactive care and communication with your healthcare providers are important for maintaining good gum health while on medications.
Diabetes and Gum Disease
Managing diabetes requires special attention to gum health as the two are closely linked due to the impact of blood sugar levels on oral health. Diabetes management plays a vital role in preventing and managing oral health complications, particularly gum disease. Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing gum disease due to poorly controlled blood sugar levels. High blood sugar provides an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive in the mouth, leading to plaque buildup and inflammation of the gums. Additionally, diabetes can weaken the body’s ability to fight infections, making gum disease more challenging to treat.
Proper management of diabetes, including monitoring blood sugar levels, following a balanced diet, and taking medications as prescribed, is essential to reduce the risk of gum disease. Regular dental check-ups, professional cleanings, and good oral hygiene practices are also crucial for individuals with diabetes to maintain healthy gums. By staying vigilant about diabetes management and oral care, individuals can lower the chances of experiencing complications related to gum disease.
Poor Nutrition
Maintaining a balanced diet is essential for preventing gum disease and promoting overall oral health. Dietary habits play an important role in the health of our gums, as nutrient deficiencies can weaken the immune system and make it harder for the body to fight off infections. Here are some key points to take into account regarding poor nutrition and its impact on gum disease:
- Inadequate Vitamin C intake: Lack of vitamin C can weaken the connective tissues in the gums, making them more susceptible to infections.
- Low Iron levels: Iron deficiency can lead to anemia, which affects the body’s ability to transport oxygen, including to the gums.
- Insufficient Vitamin D: Vitamin D is vital for calcium absorption, which is essential for maintaining strong teeth and bones.
- Excessive Sugar consumption: High sugar intake can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease.
- Lack of Antioxidants: Antioxidants help reduce inflammation in the body, including in the gums, helping to prevent gum disease.
Age and Gum Disease
Age can greatly impact the risk of developing gum disease, as oral health needs evolve with advancing years. As we age, the risk of developing gum disease increases due to various factors such as natural wear and tear on teeth and gums, medications that reduce saliva flow, and systemic diseases that affect oral health. However, there are preventive measures and dental care tips that can help reduce the risk of gum disease in older adults.
| Age Related Risk | Prevention | Dental Care Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Immunity | Regular Dental Check-ups | Brush teeth twice a day |
| Receding Gums | Good Oral Hygiene | Floss daily to remove plaque |
| Dry Mouth | Healthy Diet | Rinse with mouthwash |
| Medications Side Effects | Quit Smoking | Use a soft-bristled toothbrush |
| Diabetes Complications | Manage Stress | Stay hydrated |
Warning Signs of Gum Disease
Early detection of gum disease is essential in maintaining oral health and preventing further complications. Being aware of the warning signs can help catch gum disease in its early stages.
Here are some key indicators to watch out for:
- Bleeding Gums: Healthy gums shouldn’t bleed during regular brushing or flossing.
- Persistent Bad Breath: Bad breath that doesn’t improve with oral hygiene could be a sign of gum disease.
- Receding Gums: Gums that are pulling away from the teeth may indicate gum disease progression.
- Sensitive or Loose Teeth: Increased tooth sensitivity or teeth that feel loose could be related to gum disease.
- Swollen or Tender Gums: Gums that are swollen, tender, or discolored may be a sign of underlying issues.
Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene, and early detection of these warning signs are essential for gum disease prevention and maintaining good oral health. If you notice any of these symptoms, consult your dentist promptly for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment.
Red, Swollen Gums
Red and swollen gums are common indicators of potential gum disease and shouldn’t be ignored. When gums appear red and swollen, it’s often a sign of inflammation caused by the body’s response to harmful bacteria accumulating along the gumline. To prevent gum disease, it’s important to maintain good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups. These habits help remove plaque and tartar buildup, reducing inflammation and the risk of developing gum disease.
Incorporating proper gum disease prevention techniques into your daily routine is vital for overall oral health. Alongside regular dental visits, consider using an antiseptic mouthwash to help reduce bacteria in hard-to-reach areas. Additionally, consuming a balanced diet low in sugar and high in nutrients can support gum health.
If you notice redness and swelling in your gums, it’s important to seek professional dental advice promptly. Addressing these symptoms early on can prevent further complications and help in reducing inflammation, ultimately safeguarding your oral health.
Bleeding Gums
When gums bleed during brushing or flossing, it may signal an underlying issue that requires attention from a dental professional. Bleeding gums are often a sign of gum disease, a condition that can lead to more severe dental problems if left untreated. Here are some key points to keep in mind regarding bleeding gums:
- Importance of Gum Disease Prevention: Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups are essential in preventing gum disease and subsequent bleeding gums.
- Professional Treatment for Gum Disease: Seeking timely treatment from a dental professional can help address the underlying causes of bleeding gums and prevent further complications.
- Impact of Gum Disease on Pregnancy: Pregnant individuals are particularly vulnerable to gum disease due to hormonal changes, making regular dental care essential during this time.
- Preventive Measures for Gum Disease During Pregnancy: Maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking dental care are crucial in preventing gum disease and bleeding gums during pregnancy.
- Consultation with a Dentist: If you experience persistent bleeding gums, consulting a dentist is important to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment to safeguard your oral health.
Receding Gums
Bleeding gums can be a warning sign of gum disease, and if left untreated, this condition may progress to involve receding gums. Receding gums, also known as gingival recession, occur when the gums pull back from the tooth surface, exposing the tooth roots. This can lead to sensitivity, decay, and an unattractive smile.
Receding gums treatment is essential to prevent further damage. One common approach is the gum grafting procedure. During this surgical process, tissue is taken from the roof of the mouth or another source and attached to the areas where the gums have receded. This helps cover the exposed roots and restore the gumline.
Gum grafting can effectively reduce tooth sensitivity, improve the appearance of the smile, and protect the teeth from decay. However, early detection and intervention are vital to prevent the progression of receding gums. If you notice your gums receding, consult with a dental professional promptly to discuss the best treatment options available.
Persistent Bad Breath
Persistent bad breath, also known as halitosis, can be a source of embarrassment and may indicate underlying oral health issues. It’s essential to address this concern promptly by maintaining good oral hygiene practices and scheduling regular dental visits. Here are some key points to bear in mind:
- Proper Oral Hygiene: Brushing your teeth at least twice a day and flossing daily can help remove food particles and bacteria that contribute to bad breath.
- Hydration: Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day can help keep your mouth moist and reduce the risk of bad breath.
- Healthy Diet: Avoiding foods with strong odors such as garlic and onions can help minimize bad breath.
- Tongue Cleaning: Cleaning your tongue with a tongue scraper or your toothbrush can help eliminate odor-causing bacteria.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Visiting your dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups can help detect any underlying oral health issues that may be causing persistent bad breath.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Stress Contribute to the Development of Gum Disease?
Yes, stress can contribute to gum disease. I’ve found that managing stress through techniques like deep breathing and exercise is essential. Pairing stress management with diligent oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing, can help prevent gum issues.
How Can I Prevent Gum Disease if I Have a Family History of It?
To prevent gum disease with a family history, I focus on oral care. Daily brushing, flossing, and regular dental check-ups are essential. Knowing my genetic predisposition motivates me to be vigilant about prevention methods to maintain good oral health.
Is There a Link Between Gum Disease and Heart Conditions?
Personally, I believe maintaining good dental hygiene is key to protecting cardiovascular health. Research suggests a connection between gum disease and heart conditions. Prioritizing oral care can positively impact overall well-being.
Can Gum Disease Affect the Success of Dental Implants?
Yes, gum disease can impact dental implant success. Smoking and poor oral hygiene habits increase the risk. Inflammation and bone loss from gum disease can weaken implant stability. Regular dental check-ups and good oral care are essential for implant longevity.
Are There Natural Remedies to Help Alleviate Symptoms of Gum Disease?
In the quest for relief from gum disease symptoms, herbal remedies and essential oils offer natural support. Nutritional supplements can also aid in promoting gum health. Consider acupuncture as an alternative therapy for holistic gum care.
Conclusion
To sum up, gum disease is a common oral health issue that can be caused by factors such as poor oral hygiene, tobacco use, and genetics.
It’s important to pay attention to symptoms like red, swollen gums, bleeding gums, and receding gums, as well as persistent bad breath.
Just like a wilting flower in need of water, neglected gums can wilt and decay if not properly cared for.
Take action to prevent gum disease and maintain a healthy smile.