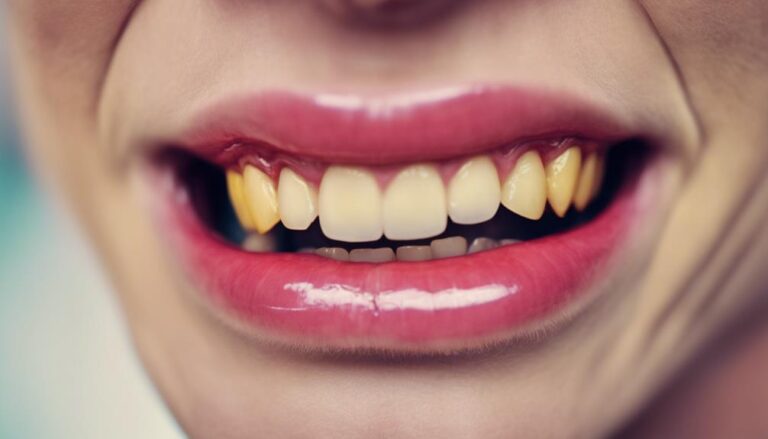
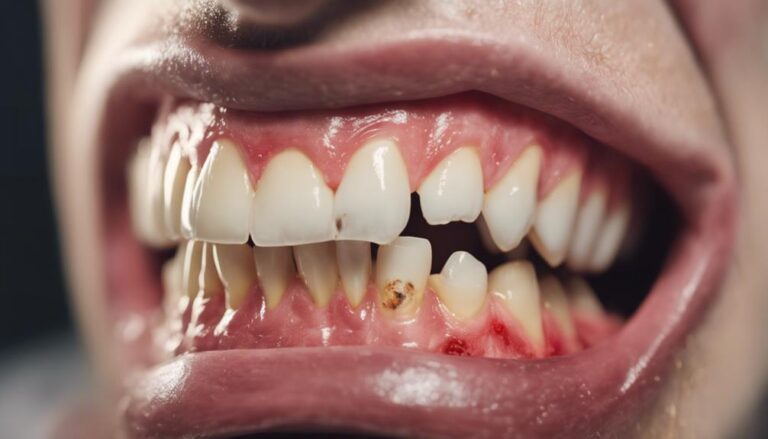
Plaque buildup and bacterial growth cause gum disease and bad breath. Maintaining oral hygiene is essential to prevent plaque accumulation, which can develop into tartar. Bacteria release toxins that lead to gum inflammation if not properly addressed. Regular cleanings and daily oral care can combat tartar buildup. Signs of gum inflammation include red, swollen, and easily bleeding gums, which may progress to periodontal disease. Monitoring these symptoms is vital for managing gum health effectively. Addressing gum issues promptly is key to preventing complications. More insights on gum disease and bad breath causes await further exploration.
Key Takeaways
- Plaque buildup and bacteria growth lead to gum disease and bad breath.
- Inflammation of the gums indicates underlying dental issues.
- Periodontal pockets form due to inflammation and infection.
- Gum recession exposes tooth roots, causing sensitivity.
- Bone loss in the jaw impacts tooth stability and oral health.
Plaque Buildup and Bacteria Growth
Plaque buildup and the growth of bacteria in the mouth play an essential role in the development of gum disease and bad breath. Maintaining oral health is vital in preventing buildup that leads to these issues. Plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, can accumulate on teeth and along the gumline. When not removed through proper oral hygiene practices like brushing and flossing, this plaque hardens into tartar, providing a breeding ground for bacteria.
These bacteria release toxins that irritate the gums, causing inflammation and eventually leading to gum disease if left untreated. Additionally, the byproducts of bacterial metabolism can result in unpleasant odors, contributing to bad breath.
To combat this, regular dental cleanings to remove tartar buildup, along with thorough daily oral care, are essential. By preventing the accumulation of plaque and bacteria through diligent oral hygiene practices, individuals can greatly reduce their risk of developing gum disease and experiencing bad breath.
Inflammation of the Gums
What role does inflammation of the gums play in the progression of gum disease and bad breath? Gum inflammation is a key indicator of underlying dental issues that can lead to more severe problems if left untreated. When gums become inflamed, they often appear red, swollen, and may bleed easily, especially during brushing or flossing. This discomfort and bleeding are signs that the gums are not healthy and that inflammation is present. Swollen gums can be a result of various factors, including poor oral hygiene, plaque buildup, or even systemic conditions.
To better understand the impact of gum inflammation, let’s explore the table below:
| Effects of Gum Inflammation | Description | Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Discomfort and Bleeding | Gums appear red, swollen, and bleed easily | Can lead to gum disease if not addressed promptly |
| Swollen Gums | Indicator of underlying dental issues | May progress to periodontal disease without treatment |
| Redness and Sensitivity | Gums become sensitive and painful | Can cause bad breath if bacterial growth is present |
Addressing gum inflammation promptly through proper oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups is essential in preventing the escalation of gum disease and halitosis.
Periodontal Pockets Formation
Periodontal pockets formation is an important occurrence in individuals with advanced gum disease, indicating a deepening of the gap between the gums and teeth, which can harbor harmful bacteria and exacerbate oral health issues. These pockets, characterized by an increased pocket depth, form when the gums pull away from the teeth due to inflammation and infection. As the gap deepens, it creates a space for plaque, tartar, and bacteria to accumulate, further irritating the gums and leading to a continuous cycle of deterioration in gum health.
Monitoring pocket depth is vital in managing gum disease as deeper pockets signify more severe disease progression. Dentists routinely measure pocket depth during check-ups using a periodontal probe. Ideally, healthy pockets should measure no more than 3mm in depth. Deeper pockets provide a sheltered environment for bacteria to thrive, contributing to ongoing inflammation and damage to the surrounding tissues. Effective oral hygiene practices, professional cleanings, and periodontal treatments are essential in addressing periodontal pockets and improving gum health.
Gum Recession
Gum recession, a common dental condition, involves the gradual loss of gum tissue around the teeth, potentially exposing the tooth roots and leading to increased sensitivity. This exposure can result from various factors, including aggressive brushing causing toothbrush abrasion or gum disease progression. Gum sensitivity is a common symptom of recession, where the roots of the teeth become more vulnerable to temperature and pressure changes.
To address gum recession, treatment options vary depending on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, improving oral hygiene practices and using desensitizing toothpaste may help alleviate symptoms. However, in more advanced cases, professional intervention such as gum grafting techniques might be necessary. Gum grafting involves taking tissue from another part of the mouth and attaching it to the affected area, helping to cover exposed roots and reduce sensitivity.
Early detection and prompt treatment of gum recession can prevent further complications and restore oral health.
Bone Loss in the Jaw
Bone loss in the jaw can greatly impact overall oral health and the stability of teeth. When bone in the jaw diminishes due to factors like advanced gum disease or tooth loss, it can lead to serious consequences. This bone serves as a foundation for teeth and supports the surrounding structures. Without an adequate amount of bone, teeth may become loose, shift, or even fall out.
In cases of significant bone loss, dental implant options can be considered to replace missing teeth. Dental implants are artificial tooth roots that are surgically placed into the jawbone, providing a sturdy base for artificial teeth. However, for successful implantation, a sufficient amount of bone is required to support the implant.
Gum grafting procedures may also be necessary to address bone loss in the jaw. This surgical technique involves taking tissue from the roof of the mouth or a donor source and grafting it onto the affected area to stimulate bone regeneration and improve overall oral health. By addressing bone loss promptly through appropriate interventions like dental implants and gum grafting, individuals can maintain the stability and functionality of their teeth.
Tooth Loss Risk Increases
With the progression of certain oral health conditions, the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene in preventing tooth loss increases substantially. Keeping up with regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups can help prevent gum disease, which is a leading cause of tooth loss. Additionally, avoiding tobacco products and consuming a balanced diet can contribute to overall oral health maintenance.
| Factors Increasing Tooth Loss Risk | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|
| Poor Oral Hygiene | Regular brushing and flossing |
| Gum Disease | Dental check-ups |
| Smoking | Avoiding tobacco products |
| Unhealthy Diet | Consuming a balanced diet |
| Lack of Dental Care | Seeking regular dental care |
Tooth loss prevention strategies also include wearing mouthguards during sports activities to prevent dental injuries and addressing issues like teeth grinding promptly. By prioritizing oral health maintenance and taking preventive measures, the risk of tooth loss can be significantly reduced, promoting overall well-being and quality of life.
Halitosis Development
What factors contribute to the development of halitosis, commonly known as bad breath? Maintaining good oral health is essential in preventing halitosis. Here are some key aspects to take into account:
- Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to the accumulation of food particles and bacteria in the mouth, causing bad breath.
- Tongue Hygiene: Neglecting to clean the tongue properly can result in a buildup of bacteria, dead cells, and debris, contributing to halitosis.
- Dry Mouth: Saliva helps cleanse the mouth, so a dry mouth due to factors like medication or mouth breathing can increase the risk of bad breath.
- Poor Dental Habits: Avoiding regular dental check-ups and cleanings can allow dental issues like gum disease or cavities to go untreated, leading to halitosis.
Foul Taste in the Mouth
Experiencing a foul taste in the mouth can be indicative of various underlying oral health issues that warrant attention and proper management. This unpleasant taste can stem from issues such as poor oral hygiene, infections, or taste bud sensitivity. Addressing the root cause is essential to alleviate this discomfort. Here are some oral hygiene tips that can help improve the taste in your mouth:
| Oral Hygiene Tips | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Brush twice a day | Removes plaque and bacteria buildup | Fresher breath |
| Floss daily | Cleans between teeth where brush can’t reach | Prevents gum disease |
| Use mouthwash | Kills bacteria and freshens breath | Reduces bad taste sensation |
Moreover, taste bud sensitivity can contribute to an altered taste perception. If you notice persistent changes in taste, consult with your dentist to rule out any underlying issues. Prioritizing good oral hygiene and seeking professional advice can help address a foul taste in the mouth effectively.
Persistent Bad Breath
Persistent bad breath, also known as halitosis, can be a distressing oral health issue that may stem from various underlying causes. When dealing with halitosis, it’s crucial to take into account factors beyond just what we eat. Here are some key points to help manage persistent bad breath effectively:
- Maintain Proper Oral Hygiene: Brushing and flossing regularly can help eliminate food particles and bacteria that lead to bad breath.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day can help keep your mouth moist and reduce odor-causing bacteria.
- Consider Tongue Scraping: Tongue scraping can help remove bacteria and debris that accumulate on the tongue, contributing to bad breath.
- Visit Your Dentist: Regular dental check-ups can help identify any underlying dental issues that may be causing bad breath.
Oral Bacteria Proliferation
Oral bacteria proliferation poses a significant risk to overall oral health and can contribute to various dental problems. Maintaining a healthy bacterial balance in the mouth is vital for excellent oral health. Certain bacteria are beneficial and help in digestion, but an overgrowth of harmful bacteria can lead to gum disease, cavities, and bad breath.
When the bacterial balance is disrupted, harmful bacteria can thrive and create an environment conducive to oral health issues. Poor oral hygiene, sugary foods, and a lack of regular dental visits can all contribute to an imbalance in oral bacteria. This imbalance can result in plaque formation, which, if not properly removed, can harden into tartar and lead to gum inflammation and disease.
To promote good oral health, it’s essential to maintain a healthy bacterial balance by practicing good oral hygiene habits, including brushing twice a day, flossing regularly, and visiting the dentist for routine check-ups. By taking these preventive measures, individuals can help prevent the proliferation of harmful bacteria and safeguard their oral health.
Sulphur Compound Production
Sulphur compounds are produced in the mouth by certain bacteria and are a common cause of bad breath. These compounds result from the breakdown of proteins by bacteria, leading to the distinct foul odor associated with bad breath. Understanding the factors influencing sulphur compound production is vital in combating bad breath effectively.
- *Dietary influences*: Foods high in protein or sugar can contribute to increased sulphur compound production.
- *Saliva production*: Adequate saliva helps wash away food particles and bacteria, reducing the buildup of sulphur compounds.
- *Genetic predisposition*: Some individuals may naturally produce more sulphur compounds due to genetic factors.
- *Mouthwash effectiveness*: Certain mouthwashes can help reduce sulphur compound levels temporarily, but long-term results may vary depending on individual oral microbiota.
Tongue Coating Buildup
The accumulation of a coating on the tongue can greatly contribute to oral health issues, including bad breath and gum disease. Proper tongue hygiene is essential to prevent the buildup of bacteria and debris that can lead to these problems.
Regularly cleaning the tongue with a tongue scraper or a soft-bristled toothbrush can help remove this coating and improve overall oral health. Additionally, incorporating mouthwash into your oral hygiene routine can provide added benefits. Mouthwashes containing antibacterial agents can help reduce the bacteria responsible for tongue coating buildup, thereby reducing the risk of bad breath and gum disease.
Maintaining good tongue hygiene not only promotes fresh breath but also supports gum health. The tongue’s surface can harbor bacteria that contribute to plaque formation and gum inflammation. By including tongue cleaning and mouthwash in your daily oral care regimen, you can effectively manage tongue coating buildup and reduce the risk of associated oral health issues.
Dry Mouth Exacerbates Symptoms
Dry mouth can worsen the symptoms associated with tongue coating buildup, potentially exacerbating bad breath and gum disease. When saliva production decreases, the mouth’s natural cleansing and antibacterial properties diminish, creating an environment where bacteria thrive and oral health issues can arise.
To mitigate these effects, hydration is important in maintaining adequate saliva flow and preventing dry mouth-related complications. Here are four essential points to keep in mind:
- Hydration Importance: Drinking a sufficient amount of water throughout the day is essential to keep saliva production at ideal levels.
- Saliva Production: Saliva plays an important role in oral health by washing away food particles, neutralizing acids, and protecting the teeth and gums.
- Prevention: Avoiding dehydrating substances like alcohol and tobacco can help prevent dry mouth and its associated consequences.
- Oral Health: Dry mouth can lead to an imbalance of bacteria in the mouth, contributing to bad breath and increasing the risk of gum disease.
Maintaining proper hydration is a simple yet effective way to support saliva production and promote good oral health.
Poor Oral Hygiene Habits
Inadequate brushing and flossing techniques can greatly contribute to the development of gum disease and bad breath. Essential brushing techniques are necessary for removing plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that accumulates on teeth. When plaque isn’t effectively removed through brushing, it can harden into tartar, leading to gum inflammation and potential gum disease. Effective brushing involves using a soft-bristled brush and gentle, circular motions to clean all tooth surfaces and along the gumline.
Equally important is flossing, as it helps remove food particles and plaque from between teeth where a toothbrush can’t reach. Flossing also stimulates the gums, promoting blood circulation and overall gum health. Failure to floss allows bacteria to thrive between teeth, increasing the risk of gum disease and contributing to persistent bad breath.
To maintain excellent oral health, it’s essential to establish a consistent oral hygiene routine that includes proper brushing techniques and regular flossing. These habits are fundamental in preventing gum disease and bad breath.
Smoking and Tobacco Use Impact
Smoking and tobacco use greatly impact oral health, worsening the risk of gum disease and persistent bad breath. Nicotine addiction resulting from smoking can have detrimental effects on dental health.
Here are some key points to take into account:
- Increased Risk of Gum Disease: Smoking weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off gum infections. This increases the likelihood of developing gum disease.
- Delayed Healing: Tobacco use can slow down the healing process post-dental procedures, leading to complications in oral health management.
- Persistent Bad Breath: The chemicals in tobacco products can linger in the mouth, causing chronic bad breath that’s challenging to eliminate.
- Stained Teeth: Smoking and tobacco can cause unsightly stains on teeth, affecting the overall aesthetics of the smile.
To mitigate these risks, tobacco cessation is essential. Implementing a robust oral hygiene routine alongside quitting smoking can significantly enhance dental health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can Stress Contribute to Gum Disease and Bad Breath?
Stress management plays a significant role in oral health. High stress levels can weaken the immune system, making gums more vulnerable to disease. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices can help combat the effects of stress on gum disease and bad breath.
Is There a Link Between Hormonal Changes and Oral Health Issues?
During pregnancy, hormonal fluctuations can impact oral health. I experienced increased gum sensitivity and bleeding while pregnant. It is crucial to maintain good oral hygiene and see a dentist regularly to address any potential issues promptly.
Can Certain Medications Worsen Symptoms of Gum Disease?
Certain medications can exacerbate symptoms of gum disease due to side effects like dry mouth or changes in gum tissue. Understanding these interactions is essential for effective treatment. Consulting with a healthcare provider helps manage medication-related oral health issues.
What Role Does Genetics Play in the Development of Periodontal Problems?
Genetic predisposition can influence periodontal problems, impacting bacterial balance in the mouth. Understanding how our genes play a role in gum health helps tailor prevention strategies. Identifying these factors early enhances oral care.
Are There Specific Foods or Drinks That Can Aggravate Bad Breath?
Staying hydrated is essential for fresh breath. Oral hygiene and diet also impact bad breath. Avoiding foods like garlic and coffee can help. Opt for water and a balanced diet for better breath.
Conclusion
To sum up, gum disease and bad breath are mainly caused by plaque buildup, bacteria growth, inflammation of the gums, formation of periodontal pockets, and other factors like poor oral hygiene habits and smoking.
It’s essential to maintain good oral hygiene practices, visit your dentist regularly, and address any symptoms promptly to prevent these issues. Remember, a healthy mouth leads to a healthier you.
So, don’t let gum disease and bad breath hold you back from living your best life!